

The V-N method measures the reflectance but inverts the beam, introducing potential asymmetric source and detector errors. V-W Method: The figure on the left shows the "V" or reference position the figure on the right shows the "W" or sampling position with the sample (S), and that one mirror flipped. The V-W method measures the square of the reflectance. Then the sample stage is pivoted, and the sample mounted for measurement. The V-W and V-N methods. These methods collect the background or reference spectrum using the exact mirrors at the same angles for the sample spectrum.Measurement is relative to a calibrated reference followed by mathematical extraction of the absolute reflectance. This is the easiest approach experimentally, but calibrated references can be expensive and need careful handling to retain their calibration.However, absolute reflection methods are employed to accurately measure the reflectance of material to derive the dielectric function and optical constants (n and k). There are several approaches to absolute reflection, all of which employ a polarizer or near-normal incidence. Most reflection measurements use a mirror or uncoated substrate for reference. This is considered a relative measurement because the spectrum of the sample is measured relative to the mirror or uncoated substrate. Most spectroscopic measurements are made relative to something. Consider transmission measurements for the simplest case. On a typical FTIR, an open beam spectrum will be collected as a background for transmission measurement. Most UV-Vis-NIR spectrometers are double-beam instruments where the rear beam serves as the reference in a typical transmission measurement, so the sample beam is measured relative to the reference beam.

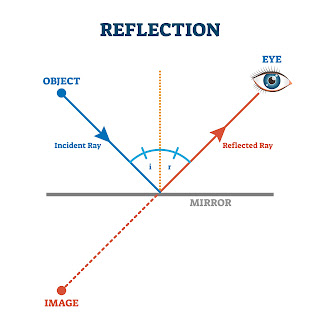
What's the difference between specular reflection and absolute reflection? The reflection from the front and back surfaces generates an interference pattern from which the thickness of the film can be determined. Specular reflectance is also used to measure free-standing non-reflective films. The measurements become less sensitive to polarization near-normal incidence (0°). Specular reflection is a mirror-like reflection from a surface. One simple example is the reflection you see in the bathroom mirror. As a spectroscopic method, specular reflection is used to characterize films on reflecting substrates and to measure the optical properties of materials.įor films deposited on a mirror-like substrate, the incident radiation transmits through the film, reflecting from the metal surface and transmitting through the film a second time. This is typically called reflection absorption or double transmission, and the spectra look comparable to transmission spectra. If the film or coating is very thin, smaller than the wavelength, then the greatest sensitivity to the film is at a grazing angle with p-polarized light. Thicker films on substrates can be measured at any angle. My work as an applications scientist at Harrick includes technical support both before and after-sales.įor example, a customer might have a flat reflecting surface and be interested in potential ways to examine it by optical spectroscopy. The most straightforward way to measure this type of sample is by specular or external reflection. Harrick Scientific manufactures mid-IR and UV-Vis-NIR spectroscopic accessories and optics for transmission, specular reflection, diffuse reflection, and ATR. Please tell us a bit about Harrick Scientific and the work you do?
#Specular reflection free
On JCassini VIMS detected a specular reflection in the north-polar region of Titan associated with Kraken Mare, one of Titan's large, presumed seas, indicating the lake's surface is smooth and free of scatterers with respect to the wavelength of 5 μ m, where VIMS detected the specular signal, strongly suggesting it is liquid.In this interview, Sue Berets, the Applications Scientist at Harrick Scientific, talks to AZoM about specular reflectance measurements and the difference between absolute and relative. This allows the Cassini optical instruments to search for specular reflections to provide further confirmation that liquids are present in these evident lakes.
As Titan progresses into northern spring, the much more numerous and larger lakes and seas in the north-polar region suggested by Cassini RADAR data, are becoming directly illuminated for the first time since the arrival of the Cassini spacecraft. After more than 50 close flybys of Titan by the Cassini spacecraft, it has become evident that features similar in morphology to terrestrial lakes and seas exist in Titan's polar regions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
